Linux内核I2C子系统驱动(二)
I2C子系统驱动之二,针对S3C2410总线驱动分析
I2C子系统驱动(二)
上一篇文章讲述了I2C子系统体系结构,总线驱动、设备驱动的知识点,下面就S3C2440 I2C总线驱动的实现详细讲解,它的源码位于drivers/i2c/busses/i2c-s3c2410.c
一、I2C平台设备资源
IIC驱动中使用的平台设备与前面看门狗、rtc等方式原理相同,但定义路径有所不同,并且设置了额外一些参数。mach_smdk2440.c文件中smdk2440_machine_init函数初始化了平台设备,还对s3c_device_i2c0平台设备进行额外的设置(s3c_i2c0_set_platdata),s3c_device_i2c0平台设备定义在arch/arm/plat-s3c/dev-i2c0.c。
static void __init smdk2440_machine_init(void)
{
s3c24xx_fb_set_platdata(&smdk2440_fb_info);
s3c_i2c0_set_platdata(NULL);
platform_add_devices(smdk2440_devices, ARRAY_SIZE(smdk2440_devices));
smdk_machine_init();
}
下面是s3c_device_i2c0平台设备相关部分,s3c_i2c0_set_platdata初始化s3c_device_i2c0.dev.platform_data为default_i2c_data0
static struct resource s3c_i2c_resource[] = {
[0] = {
.start = S3C_PA_IIC,
.end = S3C_PA_IIC + SZ_4K - 1,
.flags = IORESOURCE_MEM,
},
[1] = {
.start = IRQ_IIC,
.end = IRQ_IIC,
.flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ,
},
};
struct platform_device s3c_device_i2c0 = {
.name = "s3c2410-i2c",
#ifdef CONFIG_S3C_DEV_I2C1
.id = 0,
#else
.id = -1,
#endif
.num_resources = ARRAY_SIZE(s3c_i2c_resource),
.resource = s3c_i2c_resource,
};
static struct s3c2410_platform_i2c default_i2c_data0 __initdata = {
.flags = 0,
.slave_addr = 0x10,
.frequency = 100*1000,
.sda_delay = 100,
};
void __init s3c_i2c0_set_platdata(struct s3c2410_platform_i2c *pd)
{
struct s3c2410_platform_i2c *npd;
if (!pd)
pd = &default_i2c_data0;
npd = kmemdup(pd, sizeof(struct s3c2410_platform_i2c), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!npd)
printk(KERN_ERR "%s: no memory for platform data\n", __func__);
else if (!npd->cfg_gpio)
npd->cfg_gpio = s3c_i2c0_cfg_gpio;
s3c_device_i2c0.dev.platform_data = npd;
}
void s3c_i2c0_cfg_gpio(struct platform_device *dev)
{ // 位于arch/arm/plat-s3c24xx/setup-i2c.c
s3c2410_gpio_cfgpin(S3C2410_GPE(15), S3C2410_GPE15_IICSDA);
s3c2410_gpio_cfgpin(S3C2410_GPE(14), S3C2410_GPE14_IICSCL);
}
二、总线驱动实现
1.I2C适配器驱动加载卸载
static int s3c24xx_i2c_calcdivisor(unsigned long clkin, unsigned int wanted,
unsigned int *div1, unsigned int *divs)
{
unsigned int calc_divs = clkin / wanted;
unsigned int calc_div1;
if (calc_divs > (16*16))
calc_div1 = 512;
else
calc_div1 = 16;
calc_divs += calc_div1-1;
calc_divs /= calc_div1;
if (calc_divs == 0)
calc_divs = 1;
if (calc_divs > 17)
calc_divs = 17;
*divs = calc_divs;
*div1 = calc_div1;
return clkin / (calc_divs * calc_div1);
}
/* s3c24xx_i2c_clockrate
*
* work out a divisor for the user requested frequency setting,
* either by the requested frequency, or scanning the acceptable
* range of frequencies until something is found
*/
static int s3c24xx_i2c_clockrate(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c, unsigned int *got)
{
struct s3c2410_platform_i2c *pdata = i2c->dev->platform_data;
unsigned long clkin = clk_get_rate(i2c->clk); /* PCLK */
unsigned int divs, div1;
unsigned long target_frequency; /* 需要设置速率默认100khz */
u32 iiccon;
int freq;
i2c->clkrate = clkin;
clkin /= 1000; /* clkin now in KHz */
dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "pdata desired frequency %lu\n", pdata->frequency);
target_frequency = pdata->frequency ? pdata->frequency : 100000;
target_frequency /= 1000; /* Target frequency now in KHz */
freq = s3c24xx_i2c_calcdivisor(clkin, target_frequency, &div1, &divs); /* 计算出IICCON中Tx clock source selection和Transmit clock value */
if (freq > target_frequency) {
dev_err(i2c->dev,
"Unable to achieve desired frequency %luKHz." \
" Lowest achievable %dKHz\n", target_frequency, freq);
return -EINVAL;
}
*got = freq;
iiccon = readl(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);
iiccon &= ~(S3C2410_IICCON_SCALEMASK | S3C2410_IICCON_TXDIV_512);
iiccon |= (divs-1);
if (div1 == 512)
iiccon |= S3C2410_IICCON_TXDIV_512;
writel(iiccon, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);
if (s3c24xx_i2c_is2440(i2c)) { /* 2440设置IICLC */
unsigned long sda_delay;
if (pdata->sda_delay) {
sda_delay = (freq / 1000) * pdata->sda_delay;
sda_delay /= 1000000;
sda_delay = DIV_ROUND_UP(sda_delay, 5);
if (sda_delay > 3)
sda_delay = 3;
sda_delay |= S3C2410_IICLC_FILTER_ON;
} else
sda_delay = 0;
dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "IICLC=%08lx\n", sda_delay);
writel(sda_delay, i2c->regs + S3C2440_IICLC);
}
return 0;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_CPU_FREQ
#define freq_to_i2c(_n) container_of(_n, struct s3c24xx_i2c, freq_transition)
static int s3c24xx_i2c_cpufreq_transition(struct notifier_block *nb,
unsigned long val, void *data)
{
struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c = freq_to_i2c(nb);
unsigned long flags;
unsigned int got;
int delta_f;
int ret;
delta_f = clk_get_rate(i2c->clk) - i2c->clkrate;
/* if we're post-change and the input clock has slowed down
* or at pre-change and the clock is about to speed up, then
* adjust our clock rate. <0 is slow, >0 speedup.
*/
if ((val == CPUFREQ_POSTCHANGE && delta_f < 0) ||
(val == CPUFREQ_PRECHANGE && delta_f > 0)) {
spin_lock_irqsave(&i2c->lock, flags);
ret = s3c24xx_i2c_clockrate(i2c, &got);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&i2c->lock, flags);
if (ret < 0)
dev_err(i2c->dev, "cannot find frequency\n");
else
dev_info(i2c->dev, "setting freq %d\n", got);
}
return 0;
}
static inline int s3c24xx_i2c_register_cpufreq(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c)
{
i2c->freq_transition.notifier_call = s3c24xx_i2c_cpufreq_transition;
return cpufreq_register_notifier(&i2c->freq_transition,
CPUFREQ_TRANSITION_NOTIFIER);
}
static inline void s3c24xx_i2c_deregister_cpufreq(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c)
{
cpufreq_unregister_notifier(&i2c->freq_transition,
CPUFREQ_TRANSITION_NOTIFIER);
}
#else
static inline int s3c24xx_i2c_register_cpufreq(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c)
{
return 0;
}
static inline void s3c24xx_i2c_deregister_cpufreq(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c)
{
}
#endif
/* s3c24xx_i2c_init
*
* initialise the controller, set the IO lines and frequency
*/
static int s3c24xx_i2c_init(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c)
{
unsigned long iicon = S3C2410_IICCON_IRQEN | S3C2410_IICCON_ACKEN;
struct s3c2410_platform_i2c *pdata;
unsigned int freq;
/* get the plafrom data */
pdata = i2c->dev->platform_data; /* 获取platform_data */
/* inititalise the gpio */
if (pdata->cfg_gpio)
pdata->cfg_gpio(to_platform_device(i2c->dev));
/* write slave address */
writeb(pdata->slave_addr, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICADD);
dev_info(i2c->dev, "slave address 0x%02x\n", pdata->slave_addr);
writel(iicon, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);
/* we need to work out the divisors for the clock... */
if (s3c24xx_i2c_clockrate(i2c, &freq) != 0) { /* 设置i2c速率 */
writel(0, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);
dev_err(i2c->dev, "cannot meet bus frequency required\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
/* todo - check that the i2c lines aren't being dragged anywhere */
dev_info(i2c->dev, "bus frequency set to %d KHz\n", freq);
dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "S3C2410_IICCON=0x%02lx\n", iicon);
return 0;
}
/* s3c24xx_i2c_probe
*
* called by the bus driver when a suitable device is found
*/
static int s3c24xx_i2c_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c;
struct s3c2410_platform_i2c *pdata;
struct resource *res;
int ret;
pdata = pdev->dev.platform_data; /* 在平台设备资源中初始化了platform_data,关于platform_data参考前一节 */
if (!pdata) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "no platform data\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
i2c = kzalloc(sizeof(struct s3c24xx_i2c), GFP_KERNEL); /* s3c24xx_i2c分配空间 */
if (!i2c) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "no memory for state\n");
return -ENOMEM;
}
strlcpy(i2c->adap.name, "s3c2410-i2c", sizeof(i2c->adap.name)); /* s3c24xx_i2c初始化 */
i2c->adap.owner = THIS_MODULE;
i2c->adap.algo = &s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm; /* 通信方法,下一节重点介绍 */
i2c->adap.retries = 2;
i2c->adap.class = I2C_CLASS_HWMON | I2C_CLASS_SPD;
i2c->tx_setup = 50;
spin_lock_init(&i2c->lock);
init_waitqueue_head(&i2c->wait);
/* find the clock and enable it */
i2c->dev = &pdev->dev;
i2c->clk = clk_get(&pdev->dev, "i2c"); /* 时钟 */
if (IS_ERR(i2c->clk)) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot get clock\n");
ret = -ENOENT;
goto err_noclk;
}
dev_dbg(&pdev->dev, "clock source %p\n", i2c->clk);
clk_enable(i2c->clk);
/* map the registers */
res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0); /* 寄存器映射 */
if (res == NULL) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot find IO resource\n");
ret = -ENOENT;
goto err_clk;
}
i2c->ioarea = request_mem_region(res->start, resource_size(res),
pdev->name);
if (i2c->ioarea == NULL) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot request IO\n");
ret = -ENXIO;
goto err_clk;
}
i2c->regs = ioremap(res->start, resource_size(res));
if (i2c->regs == NULL) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot map IO\n");
ret = -ENXIO;
goto err_ioarea;
}
dev_dbg(&pdev->dev, "registers %p (%p, %p)\n",
i2c->regs, i2c->ioarea, res);
/* setup info block for the i2c core */
i2c->adap.algo_data = i2c;
i2c->adap.dev.parent = &pdev->dev;
/* initialise the i2c controller */
ret = s3c24xx_i2c_init(i2c); /* 初始化 */
if (ret != 0)
goto err_iomap;
/* find the IRQ for this unit (note, this relies on the init call to
* ensure no current IRQs pending
*/
i2c->irq = ret = platform_get_irq(pdev, 0); /* 中断申请 */
if (ret <= 0) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot find IRQ\n");
goto err_iomap;
}
ret = request_irq(i2c->irq, s3c24xx_i2c_irq, IRQF_DISABLED,
dev_name(&pdev->dev), i2c);
if (ret != 0) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot claim IRQ %d\n", i2c->irq);
goto err_iomap;
}
ret = s3c24xx_i2c_register_cpufreq(i2c); /* 关于cpufreq没明白,有关cpufreq可以暂时不管 */
if (ret < 0) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to register cpufreq notifier\n");
goto err_irq;
}
/* Note, previous versions of the driver used i2c_add_adapter()
* to add the bus at any number. We now pass the bus number via
* the platform data, so if unset it will now default to always
* being bus 0.
*/
i2c->adap.nr = pdata->bus_num;
/*调用了i2c-core中的i2c_add_adapter函数来添加一个i2c控制器,i2c_add_numbered_adapter和i2c_add_adapter的
区别在于前者用来添加一个在CPU内部集成的适配器,而后者用来添加一个CPU外部的适配器。显然这里应该用前者 */
ret = i2c_add_numbered_adapter(&i2c->adap);
if (ret < 0) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to add bus to i2c core\n");
goto err_cpufreq;
}
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, i2c);
dev_info(&pdev->dev, "%s: S3C I2C adapter\n", dev_name(&i2c->adap.dev));
return 0;
err_cpufreq:
s3c24xx_i2c_deregister_cpufreq(i2c);
err_irq:
free_irq(i2c->irq, i2c);
err_iomap:
iounmap(i2c->regs);
err_ioarea:
release_resource(i2c->ioarea);
kfree(i2c->ioarea);
err_clk:
clk_disable(i2c->clk);
clk_put(i2c->clk);
err_noclk:
kfree(i2c);
return ret;
}
/* s3c24xx_i2c_remove
*
* called when device is removed from the bus
*/
static int s3c24xx_i2c_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);
s3c24xx_i2c_deregister_cpufreq(i2c);
i2c_del_adapter(&i2c->adap); /* 删除adapter*/
free_irq(i2c->irq, i2c);
clk_disable(i2c->clk);
clk_put(i2c->clk);
iounmap(i2c->regs);
release_resource(i2c->ioarea);
kfree(i2c->ioarea);
kfree(i2c);
return 0;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_PM
static int s3c24xx_i2c_suspend_noirq(struct device *dev)
{
struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(dev);
struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);
i2c->suspended = 1;
return 0;
}
static int s3c24xx_i2c_resume(struct device *dev)
{
struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(dev);
struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);
i2c->suspended = 0;
s3c24xx_i2c_init(i2c);
return 0;
}
static struct dev_pm_ops s3c24xx_i2c_dev_pm_ops = {
.suspend_noirq = s3c24xx_i2c_suspend_noirq,
.resume = s3c24xx_i2c_resume,
};
#define S3C24XX_DEV_PM_OPS (&s3c24xx_i2c_dev_pm_ops)
#else
#define S3C24XX_DEV_PM_OPS NULL
#endif
/* device driver for platform bus bits */
static struct platform_device_id s3c24xx_driver_ids[] = {
{
.name = "s3c2410-i2c",
.driver_data = TYPE_S3C2410,
}, {
.name = "s3c2440-i2c",
.driver_data = TYPE_S3C2440,
}, { },
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(platform, s3c24xx_driver_ids);
static struct platform_driver s3c24xx_i2c_driver = {
.probe = s3c24xx_i2c_probe,
.remove = s3c24xx_i2c_remove,
.id_table = s3c24xx_driver_ids, //解释参见代码后面说明
.driver = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.name = "s3c-i2c",
.pm = S3C24XX_DEV_PM_OPS,
},
};
static int __init i2c_adap_s3c_init(void)
{
return platform_driver_register(&s3c24xx_i2c_driver);
}
subsys_initcall(i2c_adap_s3c_init);
static void __exit i2c_adap_s3c_exit(void)
{
platform_driver_unregister(&s3c24xx_i2c_driver);
}
module_exit(i2c_adap_s3c_exit);
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("S3C24XX I2C Bus driver");
MODULE_AUTHOR("Ben Dooks, <ben@simtec.co.uk>");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");i2c_adap_s3c_init注册i2c平台驱动s3c24xx_i2c_driver,它是platform_driver结构体,不要误解为i2c_driver。同时还实现了probe、remove、id_table、driver,其中suspend、resume在driver中实现。i2c_adap_s3c_exit注销s3c24xx_i2c_driver。
关于平台驱动s3c24xx_i2c_driver中名字为s3c_i2c与平台设备中名字s3c2410-i2c不一样,怎么匹配?这里主要在于id_table,s3c24xx_driver_ids包含了驱动所支持的设备ID表,判断这个表中的名字与平台设备中名字一致,则匹配成功。
2.I2C通信方法
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/i2c.h>
#include <linux/i2c-id.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/time.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/err.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/clk.h>
#include <linux/cpufreq.h>
#include <asm/irq.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#include <plat/regs-iic.h>
#include <plat/iic.h>
/* i2c controller state */
enum s3c24xx_i2c_state {
STATE_IDLE,
STATE_START,
STATE_READ,
STATE_WRITE,
STATE_STOP
};
enum s3c24xx_i2c_type {
TYPE_S3C2410,
TYPE_S3C2440,
};
struct s3c24xx_i2c {
spinlock_t lock;
wait_queue_head_t wait;
unsigned int suspended:1;
struct i2c_msg *msg;
unsigned int msg_num;
unsigned int msg_idx;
unsigned int msg_ptr;
unsigned int tx_setup;
unsigned int irq;
enum s3c24xx_i2c_state state;
unsigned long clkrate;
void __iomem *regs;
struct clk *clk;
struct device *dev;
struct resource *ioarea;
struct i2c_adapter adap;
#ifdef CONFIG_CPU_FREQ
struct notifier_block freq_transition;
#endif
};
/* default platform data removed, dev should always carry data. */
/* s3c24xx_i2c_is2440()
*
* return true is this is an s3c2440
*/
static inline int s3c24xx_i2c_is2440(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c)
{
struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(i2c->dev);
enum s3c24xx_i2c_type type;
type = platform_get_device_id(pdev)->driver_data;
return type == TYPE_S3C2440;
}
/* s3c24xx_i2c_master_complete
*
* complete the message and wake up the caller, using the given return code,
* or zero to mean ok.
*/
static inline void s3c24xx_i2c_master_complete(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c, int ret)
{
dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "master_complete %d\n", ret);
i2c->msg_ptr = 0;
i2c->msg = NULL;
i2c->msg_idx++;
i2c->msg_num = 0;
if (ret)
i2c->msg_idx = ret;
wake_up(&i2c->wait);
}
static inline void s3c24xx_i2c_disable_ack(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c)
{
unsigned long tmp;
tmp = readl(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);
writel(tmp & ~S3C2410_IICCON_ACKEN, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);
}
static inline void s3c24xx_i2c_enable_ack(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c)
{
unsigned long tmp;
tmp = readl(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);
writel(tmp | S3C2410_IICCON_ACKEN, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);
}
/* irq enable/disable functions */
static inline void s3c24xx_i2c_disable_irq(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c)
{
unsigned long tmp;
tmp = readl(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);
writel(tmp & ~S3C2410_IICCON_IRQEN, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);
}
static inline void s3c24xx_i2c_enable_irq(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c)
{
unsigned long tmp;
tmp = readl(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);
writel(tmp | S3C2410_IICCON_IRQEN, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);
}
/* s3c24xx_i2c_message_start
*
* put the start of a message onto the bus
*/
static void s3c24xx_i2c_message_start(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c,
struct i2c_msg *msg)
{
unsigned int addr = (msg->addr & 0x7f) << 1;
unsigned long stat;
unsigned long iiccon;
stat = 0;
stat |= S3C2410_IICSTAT_TXRXEN; /* 使能TXRX */
if (msg->flags & I2C_M_RD) { /* 设备地址 */
stat |= S3C2410_IICSTAT_MASTER_RX;
addr |= 1;
} else
stat |= S3C2410_IICSTAT_MASTER_TX;
if (msg->flags & I2C_M_REV_DIR_ADDR)
addr ^= 1;
/* todo - check for wether ack wanted or not */
s3c24xx_i2c_enable_ack(i2c); /* 使能ack */
iiccon = readl(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);
writel(stat, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICSTAT);
dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "START: %08lx to IICSTAT, %02x to DS\n", stat, addr);
writeb(addr, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICDS); /* 写设备地址 */
/* delay here to ensure the data byte has gotten onto the bus
* before the transaction is started */
ndelay(i2c->tx_setup);
dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "iiccon, %08lx\n", iiccon);
writel(iiccon, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);
stat |= S3C2410_IICSTAT_START; /* 启动i2c,当设备地址发送后就会进入中断,在中断中根据不同状态进行读写操作 */
writel(stat, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICSTAT);
}
static inline void s3c24xx_i2c_stop(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c, int ret)
{
unsigned long iicstat = readl(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICSTAT);
dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "STOP\n");
/* stop the transfer */
iicstat &= ~S3C2410_IICSTAT_START;
writel(iicstat, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICSTAT);
i2c->state = STATE_STOP;
s3c24xx_i2c_master_complete(i2c, ret);
s3c24xx_i2c_disable_irq(i2c);
}
/* helper functions to determine the current state in the set of
* messages we are sending */
/* 关于以下三个函数功能区别,后文详解 */
/* is_lastmsg()
*
* returns TRUE if the current message is the last in the set
*/
static inline int is_lastmsg(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c)
{
return i2c->msg_idx >= (i2c->msg_num - 1);
}
/* is_msglast
*
* returns TRUE if we this is the last byte in the current message
*/
static inline int is_msglast(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c)
{
return i2c->msg_ptr == i2c->msg->len-1;
}
/* is_msgend
*
* returns TRUE if we reached the end of the current message
*/
static inline int is_msgend(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c)
{
return i2c->msg_ptr >= i2c->msg->len;
}
/* i2s_s3c_irq_nextbyte
*
* process an interrupt and work out what to do
*/
static int i2s_s3c_irq_nextbyte(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c, unsigned long iicstat)
{
/* 此函数比较复杂,在后文中将举一个具体例子来说明整个过程 */
unsigned long tmp;
unsigned char byte;
int ret = 0;
switch (i2c->state) {
case STATE_IDLE:
dev_err(i2c->dev, "%s: called in STATE_IDLE\n", __func__);
goto out;
break;
case STATE_STOP:
dev_err(i2c->dev, "%s: called in STATE_STOP\n", __func__);
s3c24xx_i2c_disable_irq(i2c);
goto out_ack;
case STATE_START:
/* last thing we did was send a start condition on the
* bus, or started a new i2c message
*/
if (iicstat & S3C2410_IICSTAT_LASTBIT &&
!(i2c->msg->flags & I2C_M_IGNORE_NAK)) {
/* ack was not received... */
dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "ack was not received\n");
s3c24xx_i2c_stop(i2c, -ENXIO);
goto out_ack;
}
if (i2c->msg->flags & I2C_M_RD)
i2c->state = STATE_READ;
else
i2c->state = STATE_WRITE;
/* terminate the transfer if there is nothing to do
* as this is used by the i2c probe to find devices. */
if (is_lastmsg(i2c) && i2c->msg->len == 0) {
s3c24xx_i2c_stop(i2c, 0);
goto out_ack;
}
if (i2c->state == STATE_READ)
goto prepare_read;
/* fall through to the write state, as we will need to
* send a byte as well */
case STATE_WRITE:
/* we are writing data to the device... check for the
* end of the message, and if so, work out what to do
*/
if (!(i2c->msg->flags & I2C_M_IGNORE_NAK)) {
if (iicstat & S3C2410_IICSTAT_LASTBIT) {
dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "WRITE: No Ack\n");
s3c24xx_i2c_stop(i2c, -ECONNREFUSED);
goto out_ack;
}
}
retry_write:
if (!is_msgend(i2c)) {
byte = i2c->msg->buf[i2c->msg_ptr++];
writeb(byte, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICDS);
/* delay after writing the byte to allow the
* data setup time on the bus, as writing the
* data to the register causes the first bit
* to appear on SDA, and SCL will change as
* soon as the interrupt is acknowledged */
ndelay(i2c->tx_setup);
} else if (!is_lastmsg(i2c)) {
/* we need to go to the next i2c message */
dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "WRITE: Next Message\n");
i2c->msg_ptr = 0;
i2c->msg_idx++;
i2c->msg++;
/* check to see if we need to do another message */
if (i2c->msg->flags & I2C_M_NOSTART) {
if (i2c->msg->flags & I2C_M_RD) {
/* cannot do this, the controller
* forces us to send a new START
* when we change direction */
s3c24xx_i2c_stop(i2c, -EINVAL);
}
goto retry_write;
} else {
/* send the new start */
s3c24xx_i2c_message_start(i2c, i2c->msg);
i2c->state = STATE_START;
}
} else {
/* send stop */
s3c24xx_i2c_stop(i2c, 0);
}
break;
case STATE_READ:
/* we have a byte of data in the data register, do
* something with it, and then work out wether we are
* going to do any more read/write
*/
byte = readb(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICDS);
i2c->msg->buf[i2c->msg_ptr++] = byte;
prepare_read:
if (is_msglast(i2c)) {
/* last byte of buffer */
if (is_lastmsg(i2c))
s3c24xx_i2c_disable_ack(i2c);
} else if (is_msgend(i2c)) {
/* ok, we've read the entire buffer, see if there
* is anything else we need to do */
if (is_lastmsg(i2c)) {
/* last message, send stop and complete */
dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "READ: Send Stop\n");
s3c24xx_i2c_stop(i2c, 0);
} else {
/* go to the next transfer */
dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "READ: Next Transfer\n");
i2c->msg_ptr = 0;
i2c->msg_idx++;
i2c->msg++;
}
}
break;
}
/* acknowlegde the IRQ and get back on with the work */
out_ack: /* 退出时请pend flag */
tmp = readl(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);
tmp &= ~S3C2410_IICCON_IRQPEND;
writel(tmp, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);
out:
return ret;
}
/* s3c24xx_i2c_irq
*
* top level IRQ servicing routine
*/
static irqreturn_t s3c24xx_i2c_irq(int irqno, void *dev_id)
{
/* 中断第一次进入在调用s3c24xx_i2c_message_start写入设备地址后 */
struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c = dev_id;
unsigned long status;
unsigned long tmp;
status = readl(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICSTAT);
if (status & S3C2410_IICSTAT_ARBITR) {
/* deal with arbitration loss */
dev_err(i2c->dev, "deal with arbitration loss\n");
}
if (i2c->state == STATE_IDLE) {
dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "IRQ: error i2c->state == IDLE\n");
tmp = readl(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);
tmp &= ~S3C2410_IICCON_IRQPEND;
writel(tmp, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);
goto out;
}
/* pretty much this leaves us with the fact that we've
* transmitted or received whatever byte we last sent */
i2s_s3c_irq_nextbyte(i2c, status); /* 根据不同状态步步推进读写操作,i2s_s3c_irq_nextbyte难点 */
out:
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
/* s3c24xx_i2c_set_master
*
* get the i2c bus for a master transaction
*/
static int s3c24xx_i2c_set_master(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c)
{
unsigned long iicstat;
int timeout = 400;
while (timeout-- > 0) {
iicstat = readl(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICSTAT);
if (!(iicstat & S3C2410_IICSTAT_BUSBUSY))
return 0;
msleep(1);
}
return -ETIMEDOUT;
}
/* s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer
*
* this starts an i2c transfer
*/
static int s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c,
struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num)
{
unsigned long timeout;
int ret;
if (i2c->suspended)
return -EIO;
ret = s3c24xx_i2c_set_master(i2c); /* 检查i2c总线状态 */
if (ret != 0) {
dev_err(i2c->dev, "cannot get bus (error %d)\n", ret);
ret = -EAGAIN;
goto out;
}
spin_lock_irq(&i2c->lock);
i2c->msg = msgs; /* 把消息写入i2c结构体 */
i2c->msg_num = num;
i2c->msg_ptr = 0;
i2c->msg_idx = 0;
i2c->state = STATE_START;
s3c24xx_i2c_enable_irq(i2c); /* 使能中断*/
s3c24xx_i2c_message_start(i2c, msgs); /* 写设备地址,启动i2c */
spin_unlock_irq(&i2c->lock);
timeout = wait_event_timeout(i2c->wait, i2c->msg_num == 0, HZ * 5); /* 等待消息传输完成,否则超时 */
ret = i2c->msg_idx; /* 成功传输消息条数 */
/* having these next two as dev_err() makes life very
* noisy when doing an i2cdetect */
if (timeout == 0)
dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "timeout\n");
else if (ret != num) /* 如果ret不等于原有消息条数,传输失败 */
dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "incomplete xfer (%d)\n", ret);
/* ensure the stop has been through the bus */
msleep(1);
out:
return ret;
}
/* s3c24xx_i2c_xfer
*
* first port of call from the i2c bus code when an message needs
* transferring across the i2c bus.
*/
static int s3c24xx_i2c_xfer(struct i2c_adapter *adap,
struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num)
{
struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c = (struct s3c24xx_i2c *)adap->algo_data;
int retry;
int ret;
for (retry = 0; retry < adap->retries; retry++) { /* 传输不成功重复次数 */
ret = s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer(i2c, msgs, num); /* 重点在这里实现 */
if (ret != -EAGAIN)
return ret;
dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "Retrying transmission (%d)\n", retry);
udelay(100);
}
return -EREMOTEIO;
}
/* declare our i2c functionality */
static u32 s3c24xx_i2c_func(struct i2c_adapter *adap)
{ /* 支持的功能,定义在i2c.h */
return I2C_FUNC_I2C | I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_EMUL | I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING;
}
/* i2c bus registration info */
static const struct i2c_algorithm s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm = {
.master_xfer = s3c24xx_i2c_xfer,
.functionality = s3c24xx_i2c_func,
};I2C适配器的通信方法整个驱动的重点,主要实现i2c_algorithm的master_xfer()和functionality()。s3c24xx_i2c_xfer中调用了s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer,然后启动i2c,并且通过中断s3c24xx_i2c_irq和i2s_s3c_irq_nextbyte来一步步推进传输工作。
通信方法传输是以消息为单位的,所有先了解消息结构体。消息i2c_msg包括地址、标志、一条消息包含的数据及长度。
struct i2c_msg {
__u16 addr; /* slave address */
__u16 flags;
#define I2C_M_TEN 0x0010 /* this is a ten bit chip address */
#define I2C_M_RD 0x0001 /* read data, from slave to master */
#define I2C_M_NOSTART 0x4000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_REV_DIR_ADDR 0x2000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_IGNORE_NAK 0x1000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_NO_RD_ACK 0x0800 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_RECV_LEN 0x0400 /* length will be first received byte */
__u16 len; /* msg length */
__u8 *buf; /* pointer to msg data */
};
代码中提到的is_lastmsg、is_msglast、is_msgend到底判断是什么?在s3c24xx_i2c中定义的struct i2c_msg *msg看出可以包含多条消息,而一条消息有可能包含多个数据,比如对于AT24c02页写就包含多个数据。is_lastmsg判断是否是消息中最后一条,使用了变量msg_idx;is_msglast判断是否一条消息中最后一个数据,is_msgend判断是否是一条消息全部完成,所以这两个函数使用变量时msg_ptr。
下面就根据AT24C02具体的讲解s3c24xx_i2c_irq和i2s_s3c_irq_nextbyte如何实现传输。
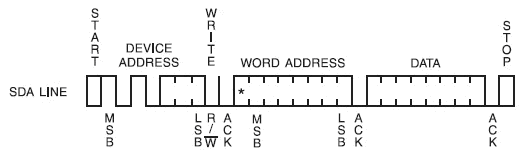
任意地址字节写时序如上所示,只需要一条消息即可。其中flag位为写,写0即可,消息包括两个数据目标地址、数据,消息如下所示。
struct i2c_msg *msg;
msg=malloc(sizeof(struct i2c_msg));
msg.len=2; // 1个目标地址和1个数据
msg.addr=0x50; // 设备地址
msg.flags=0; // write
msg.buf=(unsigned char*)malloc(2);
msg.buf[0]=0x10;// 目标地址
msg.buf[1]=0x58;// the data to write
s3c24xx_i2c_xfer中调用了s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer,在s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer中把消息传入i2c->msg,使能中断,置i2c->state 为STATE_START,调用s3c24xx_i2c_message_start启动i2c发送设备地址,就等待中断来做后续工作。当设备地址发送后就会进入中断,继续进入i2s_s3c_irq_nextbyte的STATE_START,判断消息为写,置i2c->state 为STATE_WRITE,跳入STATE_WRITE,在retry_write这一段中,if先判断是否一条消息所有数据发送完,没发送完,则每次发送一条等待下次中断进入,每发送一个数据都要清pend位;发送完else if判断是否最后一条消息,如果不是则要指针指向下一条消息继续if的步骤;最后else为发送完成,停止i2c。针对任意字节写只有一条消息,if中发送两次就完成本条消息传输。

任意地址字节读时序如上所示,需两条消息。第一条,写目标地址,flag位为写;第二条,读取数据,flag位为读,第一条与第二条消息之间要发送START。
struct i2c_msg *msgs;
msgs=malloc(2*sizeof(struct i2c_msg));
msgs[0].len=1; // 目标地址
msgs[0].addr=0x50; // 设备地址
msgs[0].flags=0; // write
msgs[0].buf=(unsigned char*)malloc(1);
msgs[0].buf[0]=0x10; // 目标地址
msgs[1].len=1; // 读出的数据
msgs[1].addr=0x50; // 设备地址
msgs[1].flags=I2C_M_RD; // read
msgs[1].buf=(unsigned char*)malloc(1);
msgs[1].buf[0]=0;// 初始化读缓冲
直接从中断开始讲,发送设备地址后,进入STATE_START,判断第一条消息为写,置i2c->state 为STATE_WRITE,跳入STATE_WRITE,第一条消息有一个数据,发送完成后,在else if中判断不是此条消息不是最后一条,就会执行else if中指向下一条消息,s3c24xx_i2c_message_start重新发送START,置i2c->state 为STATE_START。下次进入中跳到STATE_START,判断第二条消息为读,置i2c->state 为STATE_READ跳入STATE_READ,第二条消息只有一个数据,关闭ack,接收一个字节,停止i2c。看完这两个例子,再看i2s_s3c_irq_nextbyte就容易理解。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容









所有评论(0)