软件测试人员常用的Unix命令
作为一名软件测试人员,在后端测试期间,您需要具备监控服务器日志、通过分析日志找出罪魁祸首、了解进程、网络等方面的技能。一些 unix 命令在这方面非常有用。所以让我们开始探索一些有用的命令。
日期
date 命令用于查看系统时间,并使用不同的查询参数查看日期时间,例如 1995-04-28 的哪一天、2 小时前的日期时间等。
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# date
Sun Jun 12 15:53:18 +06 2022
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# date -d "1995-04-28"
Fri Apr 28 00:00:00 +06 1995
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# date --date='2 years ago'
Fri Jun 12 15:54:48 +06 2020
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# date --date='1 month ago'
Thu May 12 15:56:06 +06 2022
正常运行时间
uptime 命令可让您了解当前系统负载及其正常运行时间。
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# uptime
15:57:39 up 5:02, 0 users, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
卡
- 查看任何一年的日历
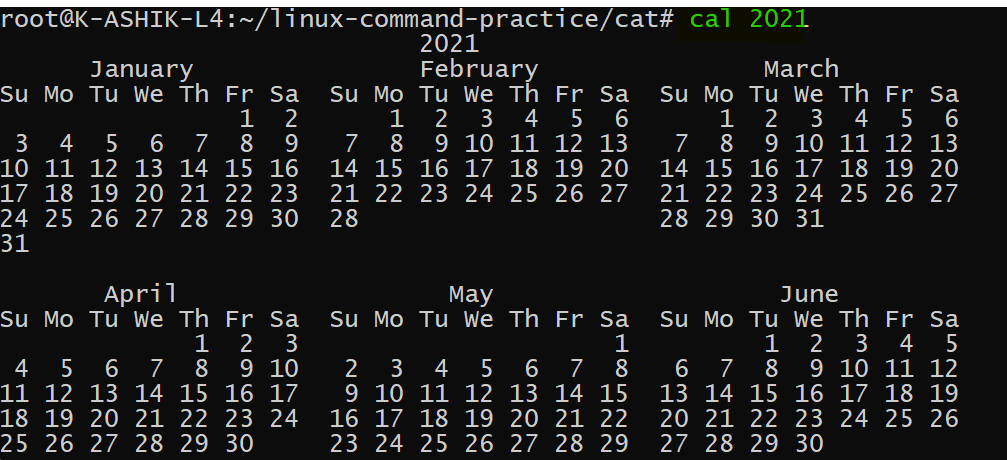
- 查看一年中任意月份的日历:cal MM YYYY
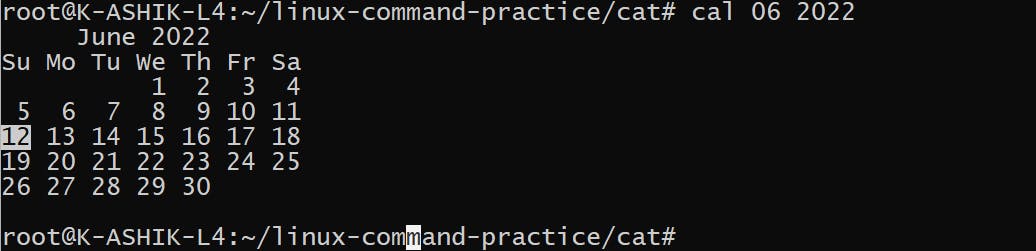
是
su(切换用户)命令用于在用户之间切换:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~# su - humayun-ashik
To run a command as administrator (user "root"), use "sudo <command>".
See "man sudo_root" for details.
humayun-ashik@K-ASHIK-L4:~$ su - root
Password:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~#
ps
ps 命令用于查看与系统上的进程相关的信息,它是“进程状态”的缩写。
- 查看当前shell的进程:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~# ps
PID TTY TIME CMD
79 pts/0 00:00:00 su
80 pts/0 00:00:03 bash
1358 pts/0 00:00:00 su
1374 pts/0 00:00:00 su
1375 pts/0 00:00:00 bash
1406 pts/0 00:00:00 ps
- 查看所有正在运行的进程
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~# ps -e
PID TTY TIME CMD
1 ? 00:00:00 init
7 ? 00:00:00 init
8 ? 00:00:02 init
9 pts/0 00:00:00 bash
79 pts/0 00:00:00 su
80 pts/0 00:00:03 bash
1358 pts/0 00:00:00 su
1359 pts/0 00:00:00 bash
1374 pts/0 00:00:00 su
1375 pts/0 00:00:00 bash
1407 pts/0 00:00:00 ps
- 查看你运行的所有进程:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~# ps -x
PID TTY STAT TIME COMMAND
1 ? Sl 0:00 /init
7 ? Ss 0:00 /init
8 ? R 0:02 /init
79 pts/0 S 0:00 su - root
80 pts/0 S 0:03 -bash
1358 pts/0 S 0:00 su - humayun-ashik
1374 pts/0 S 0:00 su - root
1375 pts/0 S 0:00 -bash
1409 pts/0 R+ 0:00 ps -x
- 使用 -f 选项查看完整格式列表:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~# ps -ef
UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD
root 1 0 0 10:55 ? 00:00:00 /init
root 7 1 0 10:55 ? 00:00:00 /init
root 8 7 0 10:55 ? 00:00:02 /init
humayun+ 9 8 0 10:55 pts/0 00:00:00 -bash
root 79 9 0 10:58 pts/0 00:00:00 su - root
root 80 79 0 10:58 pts/0 00:00:03 -bash
root 1358 80 0 17:06 pts/0 00:00:00 su - humayun-ashik
humayun+ 1359 1358 0 17:06 pts/0 00:00:00 -bash
root 1374 1359 0 17:07 pts/0 00:00:00 su - root
root 1375 1374 0 17:07 pts/0 00:00:00 -bash
root 1410 1375 0 17:23 pts/0 00:00:00 ps -ef
杀
kill 命令用于手动终止进程。 kill 命令向进程发送信号,终止该进程
- 查看所有信号:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~# kill -l
1) SIGHUP 2) SIGINT 3) SIGQUIT 4) SIGILL 5) SIGTRAP
6) SIGABRT 7) SIGBUS 8) SIGFPE 9) SIGKILL 10) SIGUSR1
11) SIGSEGV 12) SIGUSR2 13) SIGPIPE 14) SIGALRM 15) SIGTERM
16) SIGSTKFLT 17) SIGCHLD 18) SIGCONT 19) SIGSTOP 20) SIGTSTP
21) SIGTTIN 22) SIGTTOU 23) SIGURG 24) SIGXCPU 25) SIGXFSZ
26) SIGVTALRM 27) SIGPROF 28) SIGWINCH 29) SIGIO 30) SIGPWR
31) SIGSYS 34) SIGRTMIN 35) SIGRTMIN+1 36) SIGRTMIN+2 37) SIGRTMIN+3
38) SIGRTMIN+4 39) SIGRTMIN+5 40) SIGRTMIN+6 41) SIGRTMIN+7 42) SIGRTMIN+8
43) SIGRTMIN+9 44) SIGRTMIN+10 45) SIGRTMIN+11 46) SIGRTMIN+12 47) SIGRTMIN+13
48) SIGRTMIN+14 49) SIGRTMIN+15 50) SIGRTMAX-14 51) SIGRTMAX-13 52) SIGRTMAX-12
53) SIGRTMAX-11 54) SIGRTMAX-10 55) SIGRTMAX-9 56) SIGRTMAX-8 57) SIGRTMAX-7
58) SIGRTMAX-6 59) SIGRTMAX-5 60) SIGRTMAX-4 61) SIGRTMAX-3 62) SIGRTMAX-2
63) SIGRTMAX-1 64) SIGRTMAX
- 使用 pid 杀死任何进程:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~# ps
PID TTY TIME CMD
79 pts/0 00:00:00 su
80 pts/0 00:00:03 bash
1358 pts/0 00:00:00 su
1374 pts/0 00:00:00 su
1375 pts/0 00:00:00 bash
1413 pts/0 00:00:00 ps
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~# kill 1413
- 对于强杀:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~# ps -ef
UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD
root 1 0 0 10:55 ? 00:00:00 /init
root 7 1 0 10:55 ? 00:00:00 /init
root 8 7 0 10:55 ? 00:00:02 /init
humayun+ 9 8 0 10:55 pts/0 00:00:00 -bash
root 79 9 0 10:58 pts/0 00:00:00 su - root
root 80 79 0 10:58 pts/0 00:00:03 -bash
root 1358 80 0 17:06 pts/0 00:00:00 su - humayun-ashik
humayun+ 1359 1358 0 17:06 pts/0 00:00:00 -bash
root 1374 1359 0 17:07 pts/0 00:00:00 su - root
root 1375 1374 0 17:07 pts/0 00:00:00 -bash
root 1415 1375 0 17:35 pts/0 00:00:00 ps -ef
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~# kill -9 1374
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~# Killed
平
-ping 命令用于了解从您的机器到任何目标服务器的连接状态
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~# ping google.com
PING google.com (74.125.24.102) 56(84) bytes of data.
From 192.168.43.1 (192.168.43.1) icmp_seq=16 Destination Net Unreachable
^C
--- google.com ping statistics ---
25 packets transmitted, 0 received, +1 errors, 100% packet loss, time 25034ms
pipe 2
免费
free 命令提供有关物理和交换内存的总量,以及空闲和已用内存和空闲内存的信息。
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice# free
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 5022200 87728 4758416 72 176056 4726356
Swap: 2097152 0 2097152
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice# free -h
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 4.8Gi 85Mi 4.5Gi 0.0Ki 171Mi 4.5Gi
Swap: 2.0Gi 0B 2.0Gi
从
du(Disk Usage)是标准的Unix/Linux命令,用于查看文件和目录的磁盘使用信息。
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice# du -h grep/
8.0K grep/grepfolder
16K grep/
自由度
df 代表“磁盘文件系统”,用于显示文件系统中使用的磁盘空间。
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sdb 251G 1.8G 237G 1% /
none 2.4G 4.0K 2.4G 1% /mnt/wsl
tools 223G 111G 112G 50% /init
none 2.4G 0 2.4G 0% /dev
none 2.4G 8.0K 2.4G 1% /run
none 2.4G 0 2.4G 0% /run/lock
none 2.4G 0 2.4G 0% /run/shm
none 2.4G 0 2.4G 0% /run/user
tmpfs 2.4G 0 2.4G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
drivers 223G 111G 112G 50% /usr/lib/wsl/drivers
lib 223G 111G 112G 50% /usr/lib/wsl/lib
drvfs 223G 111G 112G 50% /mnt/c
drvfs 366G 28G 339G 8% /mnt/d
drvfs 366G 20G 347G 6% /mnt/e
密码
pwd 代表打印工作目录。该命令包含在 /usr/bin/pwd 中。 它经常用于了解当前目录位置。
root@K-ASHIK-L4:/usr/bin# pwd
/usr/bin
清除
要清除当前终端文本,使用 clear 命令。只需编写 clear 并按回车键即可清除终端文本。
mkdir
使用 mkdir 创建目录。
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice# mkdir dir1
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice# ls -l
total 4
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 12 11:31 dir1
它还可以用于一次创建多个目录:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice# mkdir dir2 dir3 dir4
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice# ls -l
total 16
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 12 11:31 dir1
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 12 11:34 dir2
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 12 11:34 dir3
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 12 11:34 dir4
光盘
cd 命令用于更改工作目录。
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice# pwd
/root/linux-command-practice
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice# cd dir1
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/dir1#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/dir1#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/dir1# pwd
/root/linux-command-practice/dir1
在更改之前,工作目录是 /root/linux-command-practice 并且在更改工作目录之后是 /root/linux-command-practice/dir1
要返回上一个目录,我们可以使用 cd ..
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/dir1# pwd
/root/linux-command-practice/dir1
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/dir1# cd ..
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice# pwd
/root/linux-command-practice
我们还可以通过提及它的路径来转到任何目录:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice# ls
dir1 dir2 dir3 dir4
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice# cd dir2
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/dir2#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/dir2# cd ../dir4
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/dir4#
这里工作目录中有 4 个目录 - dir1 dir2 dir3 dir4。首先我们移动到 dir2 目录,然后从 dir2 转到 dir4。
触摸
touch 命令用于创建没有内容的文件。
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/touch# ls -l
total 0
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/touch# touch file1.txt
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/touch#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/touch# ls -l
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 12 11:58 file1.txt
我们可以一次使用多个空文件:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/touch# touch file2.txt logfile.log csvfile.csv
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/touch#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/touch# ls -l
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 12 12:00 csvfile.csv
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 12 11:58 file1.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 12 12:00 file2.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 12 12:00 logfile.log
我们可以通过以下方式创建具有任何时间戳的文件:touch -t YYYYMMDDHHMM fileName
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/touch# touch -t 202105111212 time.txt
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/touch#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/touch# ls -l
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 12 12:00 csvfile.csv
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 12 11:58 file1.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 12 12:00 file2.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 12 12:00 logfile.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 May 11 2021 time.txt
猫
cat (concatenate) 命令是非常常用的命令。它读取文件的内容并显示为输出。
cat 命令的一些用法如下:
- 创建有一些内容的文件:添加完内容后使用Ctrl+D退出。
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat > filewithcontent.txt
line1
line2
line3
line4
- 查看文件内容:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat filewithcontent.txt
line1
line2
line3
line4
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
- 查看多个文件的内容:按顺序连接文件内容并显示输出。
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat filewithcontent.txt anotherfile.log
line1
line2
line3
line4
anotherfile-line-1
anotherfile-line-2
anotherfile-line-3
anotherfile-line-4
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat anotherfile.log filewithcontent.txt
anotherfile-line-1
anotherfile-line-2
anotherfile-line-3
anotherfile-line-4
line1
line2
line3
line4
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
- 在内容中显示行号:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat -n filewithcontent.txt
1 line1
2 line2
3 line3
4 line4
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
- 将一个文件的内容替换为另一个:cat anotherfile.log > filewithcontent.txt 这里文件filewithcontent.txt 的内容替换为anotherfile.log 文件的内容。
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat filewithcontent.txt
line1
line2
line3
line4
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat anotherfile.log
anotherfile-line-1
anotherfile-line-2
anotherfile-line-3
anotherfile-line-4
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat anotherfile.log > filewithcontent.txt
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat filewithcontent.txt
anotherfile-line-1
anotherfile-line-2
anotherfile-line-3
anotherfile-line-4
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
- 将一个文件的标准输出附加到另一个文件的末尾:cat filewithcontent.txt >> outputfile.log
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat outputfile.log
This is output file, you can append here
>
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat filewithcontent.txt >> outputfile.log
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat outputfile.log
This is output file, you can append here
>
anotherfile-line-1
anotherfile-line-2
anotherfile-line-3
anotherfile-line-4
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
- 附加多个文件的内容并将所有输出插入新文件:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# ls
logfile.log outputfile.log test1.log test2.txt
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat test1.log
line-1
line-2
line-3
line-4
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat test2.txt
anotherfile-line-1
anotherfile-line-2
anotherfile-line-3
anotherfile-line-4
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat test1.log test2.txt > test3.log
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# ls
logfile.log outputfile.log test1.log test2.txt test3.log
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat test3.log
line-1
line-2
line-3
line-4
anotherfile-line-1
anotherfile-line-2
anotherfile-line-3
anotherfile-line-4
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
- 创建隐藏文件:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat > .hiddenfile.txt
This is a hidden file
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
毫伏
mv 命令用于重命名文件。
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice# ls
cat dir1 dir100 dir2 dir3 grep touch
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice# mv dir100 mv-command
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice# ls
cat dir1 dir2 dir3 grep mv-command touch
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice#
rm
rm 命令用于删除文件。
- 请求删除权限:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# rm -i test2.txt
rm: remove regular file 'test2.txt'? y
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# ls
catdir logfile.log.gz numbers.txt outputfile.log test1.log test3.log
- 强制删除:未请求权限
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# ls
catdir logfile.log.gz numbers.txt outputfile.log test1.log test3.log
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# rm -f test1.log
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# ls
catdir logfile.log.gz numbers.txt outputfile.log test3.log
- 删除所有扩展名为 .log 的文件:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# ls
catdir logfile.log.gz numbers.txt outputfile.log test3.log
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# rm *log
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# ls
catdir logfile.log.gz numbers.txt
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
- 递归删除文件和目录:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# ls
catdir logfile.log.gz numbers.txt willbedeleted
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# rm -r *
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# ls
是 RM##
dir 命令用于删除空目录,如果目录不为空则抛出错误。
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~# rmdir linux-command-practice
rmdir: failed to remove 'linux-command-practice': Directory not empty
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/rmdir# ls
rmdir1 rmdir2
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/rmdir# rmdir -v rmdir1
rmdir: removing directory, 'rmdir1'
这里 -v 选项用于在删除目录时获取详细信息。
- 删除所有目录:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/rmdir# ls
rmdir2 rmdir3 rmdir4 rmdir5 rmdir6 rmdir7
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/rmdir# rmdir -v *
rmdir: removing directory, 'rmdir2'
rmdir: removing directory, 'rmdir3'
rmdir: removing directory, 'rmdir4'
rmdir: removing directory, 'rmdir5'
rmdir: removing directory, 'rmdir6'
rmdir: removing directory, 'rmdir7'
cp
cp 命令用于将文件从一个源复制到目标。
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/touch# ls
csvfile.csv file1.txt file2.txt logfile.log time.txt
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/touch# cp /root/linux-command-practice/touch/*.txt /root/linux-command-practice/cat/
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/touch# ls -l ../cat/
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 12 16:53 file1.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 12 16:53 file2.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 12 16:53 time.txt
- 使用 cp -r 选项我们可以复制包含所有内容的目录:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice# cp -r grep dir1
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice# cd dir1
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/dir1# ls
grep
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/dir1# cd grep/
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/dir1/grep# ls
grepPracticeLog.log grepfolder
LS
- 列出文件和目录:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# ls
catdir logfile.log outputfile.log test1.log test2.txt test3.log
- 列出文件或目录及其大小:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# ls -s
total 24
4 catdir 4 logfile.log 4 outputfile.log 4 test1.log 4 test2.txt 4 test3.log
- 以长格式列出文件:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# ls -l
total 24
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 12 13:00 catdir
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1184 Jun 12 12:26 logfile.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 122 Jun 12 12:45 outputfile.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 28 Jun 12 12:49 test1.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 76 Jun 12 12:31 test2.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 104 Jun 12 12:50 test3.log
这里第一列代表内容权限,第二列代表否。链接数,第 3 列所有者,第 4 组所有者 第 5 个字节大小,第 6 个修改日期,第 7 个是文件/目录名称。
- 列出文件,包括隐藏文件:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# ls -al
total 36
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Jun 12 13:00 .
drwxr-xr-x 8 root root 4096 Jun 12 12:16 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 22 Jun 12 12:57 .hiddenfile.txt
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 12 13:00 catdir
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1184 Jun 12 12:26 logfile.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 122 Jun 12 12:45 outputfile.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 28 Jun 12 12:49 test1.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 76 Jun 12 12:31 test2.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 104 Jun 12 12:50 test3.log
- 列表文件按大小降序排列:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# ls -lS
total 24
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 12 13:00 catdir
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1184 Jun 12 12:26 logfile.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 122 Jun 12 12:45 outputfile.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 104 Jun 12 12:50 test3.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 76 Jun 12 12:31 test2.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 28 Jun 12 12:49 test1.log
- 列表文件按大小升序排序:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# ls -lrS
total 24
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 28 Jun 12 12:49 test1.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 76 Jun 12 12:31 test2.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 104 Jun 12 12:50 test3.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 122 Jun 12 12:45 outputfile.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1184 Jun 12 12:26 logfile.log
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 12 13:00 catdir
- 列表文件按日期时间降序排序:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# ls -lt
total 24
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 12 13:00 catdir
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 104 Jun 12 12:50 test3.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 28 Jun 12 12:49 test1.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 122 Jun 12 12:45 outputfile.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 76 Jun 12 12:31 test2.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1184 Jun 12 12:26 logfile.log
- 列表文件按日期时间升序排序
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# ls -lrt
total 24
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1184 Jun 12 12:26 logfile.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 76 Jun 12 12:31 test2.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 122 Jun 12 12:45 outputfile.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 28 Jun 12 12:49 test1.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 104 Jun 12 12:50 test3.log
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 12 13:00 catdir
- 以可读大小格式列出文件:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# ls -lh
total 24K
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4.0K Jun 12 13:00 catdir
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1.2K Jun 12 12:26 logfile.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 122 Jun 12 12:45 outputfile.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 28 Jun 12 12:49 test1.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 76 Jun 12 12:31 test2.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 104 Jun 12 12:50 test3.log
- 以可读大小格式和时间戳升序列出所有扩展名为 .log 的文件:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# ls -lrth *.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1.2K Jun 12 12:26 logfile.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 122 Jun 12 12:45 outputfile.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 28 Jun 12 12:49 test1.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 104 Jun 12 12:50 test3.log
厕所
wc 命令代表字数。它用于找出指定文件中的行数、字数、字节数和字符数。
- 打印文件中的行数:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# wc -l logfile.log
37 logfile.log
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
- 打印文件中的字数:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat test1.log
line-1 colum2
line-2 column2
line-3 column2
line-4 column2
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# wc -w test1.log
8 test1.log
- 显示字符数:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# wc -c test1.log
59 test1.log
唯一
uniq 命令用于从文件中获取唯一或重复的行。
-d 显示重复行 -u 显示唯一行 -c 计算每个单词在文件中出现的次数
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat test1.log
line-1 colum2
line-2 column2
line-3 column2
line-4 column2
line-4 column2
line-4 column2
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# uniq -c test1.log
1 line-1 colum2
1 line-2 column2
1 line-3 column2
3 line-4 column2
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# uniq -d test1.log
line-4 column2
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# uniq -u test1.log
line-1 colum2
line-2 column2
line-3 column2
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
头
head 命令用于查看前 n 行内容。
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# head -3 logfile.log
"201000225","00000000",10100066
"201000228","00000000",10100069
"202000231","00000000",10200072
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# head -5 logfile.log
"201000225","00000000",10100066
"201000228","00000000",10100069
"202000231","00000000",10200072
"202000234","00000000",10200075
"203000240","00000000",10300078
尾
tail 命令用于查看最后 n 行内容。
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# tail -2 logfile.log
"218000382","00000000",11800171
"218000383","00000000",11800174
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# tail -5 logfile.log
"216000369","00000000",11600162
"217000375","00000000",11700165
"217000378","00000000",11700168
"218000382","00000000",11800171
"218000383","00000000",11800174
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
- 使用头部和尾部打印第 26-30 行:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat logfile.log | head -30 | tail -5
"213000339","00000000",11300141
"213000342","00000000",11300144
"214000348","00000000",11400147
"214000351","00000000",11400150
"215000357","00000000",11500153
切
cut 命令用于从文件中剪切所需的文本。它可以剪切列和字段上的数据。
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat test1.log
line-1 colum2
line-2 column2
line-3 column2
line-4 column2
line-4 column2
line-4 column2
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cut -c5 test1.log
-
-
-
-
-
-
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cut -f2 test1.log
colum2
column2
column2
column2
column2
column2
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
排序
- 排序号码
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat numbers.txt
2
4
1
54
32
-4
9
100
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# sort -n numbers.txt
-4
1
2
4
9
32
54
100
- 对文本文件进行排序
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# cat test3.log
第 1 行
第 2 行
第 3 行
第 4 行
anotherfile-line-1
另一个文件第 2 行
另一个文件第 3 行
另一个文件第 4 行
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# sort test3.log
anotherfile-line-1
另一个文件第 2 行
另一个文件第 3 行
另一个文件第 4 行
第 1 行
第 2 行
第 3 行
第 4 行
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat#
- 以相反的顺序对第 3 列的值进行排序:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/cat# sort -rk 3n logfile.log
"218000383","000",11800174
"218000382","000",11800171
"217000378","000",11700168
"217000375","000",11700165
grep
grep 命令用于在文件中搜索所需的模式。
- 不区分大小写的搜索
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/grep# grep -i "jmeter" grepPracticeLog.log
2. Download apache Jmeter latest version and extract
6. Then place extracted jar file into your jmeter /lib/ext directory.
7. Start JMETER and write API test script for following two cases: Here email must be generated from your jar file which you have performed in step 6 and 7.
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/grep#
这里 -i 选项将不区分大小写地在日志文件中搜索 "" 中的字符串。
- 计算出现次数
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/grep# grep -c "jmeter" grepPracticeLog.log
1
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/grep# grep -ic "jmeter" grepPracticeLog.log
3
- 搜索全词匹配:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/grep# grep -w "JMETER" grepPracticeLog.log
7. Start JMETER and write API test script for following two cases: Here email must be generated from your jar file which you have performed in step 6 and 7.
- 只显示匹配的模式:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/grep# cat grepPracticeLog.log
1. Setup Intellij IDEA
2. Download apache Jmeter latest version and extract
3. Create a java project in Intellij IDEA
4. Write a class GenerateRandomEmail and inside this class create a method getRandomEmail() which should return any random valid email.
5. Make a jar file from Intellij IDEA of your written project which you have performed in step 3 and 4.
6. Then place extracted jar file into your jmeter /lib/ext directory.
7. Start JMETER and write API test script for following two cases: Here email must be generated from your jar file which you have performed in step 6 and 7.
Case - 1: User registration with valid email.
Case - 2: User registration with already registered email.
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/grep#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/grep#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/grep#
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/grep# grep -o "Case" grepPracticeLog.log
Case
Case
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/grep#
- 打印不包含字符串的行:
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/grep# grep -v "email" grepPracticeLog.log
1. Setup Intellij IDEA
2. Download apache Jmeter latest version and extract
3. Create a java project in Intellij IDEA
5. Make a jar file from Intellij IDEA of your written project which you have performed in step 3 and 4.
6. Then place extracted jar file into your jmeter /lib/ext directory.
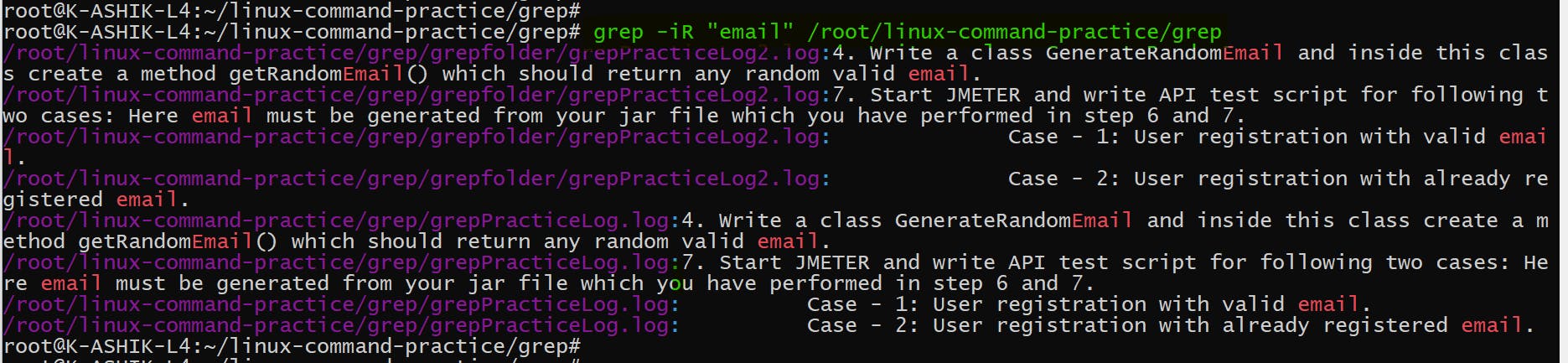
- 使用 grep -R 选项递归搜索所有文件和目录:
压缩包
gzip 用于制作 zip 文件
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/touch# gzip csvfile.csv
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/touch# ls
csvfile.csv.gz file1.txt file2.txt logfile.log time.txt
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/touch# gzip -r *
root@K-ASHIK-L4:~/linux-command-practice/touch# ls
csvfile.csv.gz file1.txt.gz file2.txt.gz logfile.log.gz time.txt.gz
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献12493条内容
已为社区贡献12493条内容










所有评论(0)