Spring学习心得(5)-- spring容器创建对象的生命周期
IOC的概念:把对象的创建、初始化、销毁等工作交给spring容器来完成。对象的创建我们在前面几个例子已经讨论到了,现在,我们来讨论一下对象的初始化,销毁对象的初始化和销毁,也是有spring来完成,可是我们之前在执行的时候,没有看见它们的踪影。 对于了解这个问题,可以设置spring的配置文件的bean中的init-method和destroy-method的
IOC的概念:
把对象的创建、初始化、销毁等工作交给spring容器来完成。
对象的创建我们在前面几个例子已经讨论到了,现在,我们来讨论一下
对象的初始化,销毁
对象的初始化和销毁,也是有spring来完成,可是我们之前在执行的时候,没有看见它们的踪影。
对于了解这个问题,可以设置spring的配置文件的bean中的init-method和destroy-method的取值。
首先,我们要在相应的类中创建好初始化及销毁的方法。名字可以任意取,因为等下要配置到配置文件中。
类中的代码:
public class helloSpring implements Serializable {
//客户端掉用这个方法
public void hello(){
System.out.println("hello spring!");
}
//默认构造函数
public helloSpring() {
System.out.println("new instance");
}
//初始化调用这个方法
public void init(){
System.out.println("init+++++++++++++++++");
}
//摧毁调用这个方法
public void destory(){
System.out.println("destory-----------------");
}
}<!--
init-method:指该bean对应的类中的初始化调用的方法
destroy-method:指该bean对应的类中的摧毁调用的方法
-->
<bean class="cn.ansel.domain.helloSpring" id="hello" init-method="init" destroy-method="destory" ></bean>public class testHelloSpring {
/**
* 测试对象的创建、初始化、摧毁是否由spring完成
*/
@Test
public void test1(){
//启动spring容器
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//得到helloSpring对象
helloSpring helloSpring=(helloSpring) applicationContext.getBean("hello");
//调用该对象的方法
helloSpring.hello();
}
}运行测试类的结果
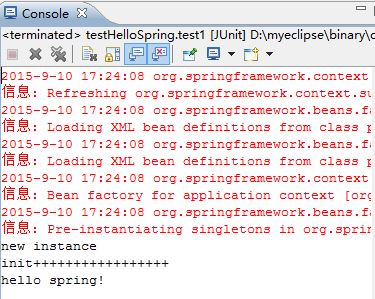
从运行结果我们可以看到,spring容器一开启之后,就创建bean的对象,然后再执行初始化方法,然后由客户端调用相应的方法。可是在这里,我们没有看到spring容器调用它的摧毁方法。
我们在调用完hello方法之后,再调用close方法,却找不到。
针对这个问题,我们只需要将applicationContext向下转型之后,就可以调用其摧毁方法了。
修改完代码之后:
public class testHelloSpring {
/**
* 测试对象的创建、初始化、摧毁是否由spring完成
*/
@Test
public void test1(){
//启动spring容器
ApplicationContext Context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//得到helloSpring对象
helloSpring helloSpring=(helloSpring) Context.getBean("hello");
//调用该对象的方法
helloSpring.hello();
//把上面得到的context向下转型
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext=(ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)Context;
//关闭spring容器
applicationContext.close();
}
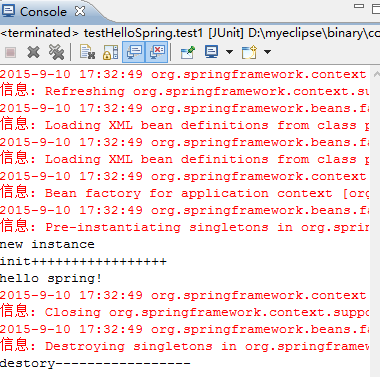
} 再次运行,
当关闭spring容器的时候,spring容器调用destory方法。
多例对象的生命周期:
当我们把配置文件中的scope取值变成多例的时候,看看程序会怎样运行:
配置文件的代码:
<bean class="cn.ansel.domain.helloSpring" id="hello" init-method="init" destroy-method="destory" scope="prototype"></bean> 相关类和测试类的代码不变,然后运行测试类:
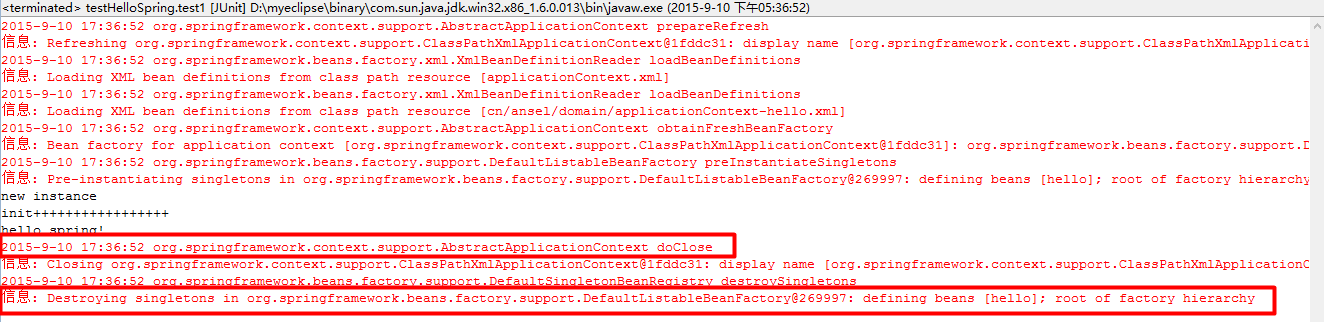
从运行结果我们可以看到,在多例的情况下没有执行destory方法,但是看运行结果图可以知道,spring容器确实是调用了关闭的方法。并且下面那句话是摧毁单例对象,并没有摧毁多例对象。
总结:
spring容器的生命周期:
(a)在单例情况下:
1、由spring容器创建对象
2、spring容器调用初始化方法
3、客户点调用该对象的某些方法
4、关闭spring容器的时候,执行摧毁方法
(b)在多例的情况下:
1、由spring容器创建对象
2、spring容器调用初始化方法
3、客户点调用该对象的某些方法
Init和destroy
说明:
1、 init方法是由spring内部执行的
2、 只有当spring容器关闭以后才能执行destroy方法,spring容器一般情况下是不会关闭的。只有当web容器销毁掉的时候才可能关闭掉,所以只要一个对象在spring容器中,在spring容器关闭之前,会一直保留。
3、 如果一个bean的配置是scope为”prototype”,则spring容器不负责销毁。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容







所有评论(0)