Swing超基础学习总结——2、简单布局:FlowLayout、GridLayout、BorderLayout、BoxLayout
其中重要讲三种布局,依靠的是JFrame容器FlowLayout案例构造参数说明BorderLayout案例构造参数说明BoxLayout案例构造参数说明FlowLayout最简单的布局管理器。它按照和页面上排列单词的类似方式来安排组件—-从左到右,直至没有多余的空间,然后转到下一行案例:public static void main(String[] args) {
·
其中重要讲三种布局,依靠的是JFrame容器
FlowLayout
最简单的布局管理器。它按照和页面上排列单词的类似方式来安排组件—-从左到右,直至没有多余的空间,然后转到下一行
案例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Layout测试");
frame.setSize(300, 300);
//FlowLayout构造参数见下面
frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.CENTER, 10, 10));
//对齐方式可以只添加一个JButton测试,间隙需要多个JButton才能看出明显的效果
frame.add(new JButton("首页"));
frame.add(new JButton("信息"));
frame.add(new JButton("查看"));
frame.add(new JButton("退出"));
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
}构造参数说明:
无参:默认居中,水平与垂直间隙默认为5个单位
一个参数:修改控件对其方式,水平与垂直间隙默认为5个单位
三个参数:分别为修改控件对其方式,修改水平间隙,修改垂直间隙
GridLayout
建立一个组件表格,并且当组件加入时,会依序又左至右,由上至下填充到每个格子,它不能由你指定想放那个格子就放那个格子
案例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame();
frame.setTitle("GridLayout测试");
frame.setSize(300, 300);
frame.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 3));
JButton bt;
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
bt = new JButton("" + (i + 1));
frame.add(bt);
}
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
}构造参数说明:
无参:默认一行一列
两个参数:分别设置行数和列数
四个参数:分别设置行数,列数,水平间距,垂直间距
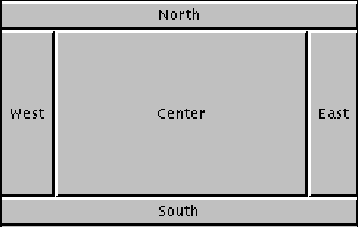
BorderLayout
使其符合下列五个区域:北、南、东、西、中。每个区域最多只能包含一个组件
案例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("BorderLayout测试");
frame.setSize(300, 300);
frame.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
JButton north_bt = new JButton("北");
JButton south_bt = new JButton("南");
JButton east_bt = new JButton("东");
JButton west_bt = new JButton("西");
JButton center_bt = new JButton("中");
frame.add(north_bt, BorderLayout.NORTH);
frame.add(south_bt, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
frame.add(east_bt, BorderLayout.EAST);
frame.add(west_bt, BorderLayout.WEST);
frame.add(center_bt, BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
}构造参数说明:
无参:组件之间无边距
两个参数:分别设置组件之间水平,垂直的边距
注:容器添加控件时的add方法参数的区别
BoxLayout
允许垂直或水平布置多个组件的布局管理器
案例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("BoxLayout测试");
frame.setSize(300, 300);
frame.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
JPanel xPanel = new JPanel();
JPanel yPanel = new JPanel();
//详见下面的构造参数说明
xPanel.setLayout(new BoxLayout(xPanel, BoxLayout.X_AXIS));
yPanel.setLayout(new BoxLayout(yPanel, BoxLayout.Y_AXIS));
JButton bt1 = new JButton("1");
JButton bt2 = new JButton("2");
JButton bt3 = new JButton("3");
JButton bt4 = new JButton("4");
// xPanel.add(bt1);
// xPanel.add(bt2);
// xPanel.add(bt3);
// xPanel.add(bt4);
//frame.add(xPanel, BorderLayout.PAGE_START);
yPanel.add(bt1);
yPanel.add(bt2);
yPanel.add(bt3);
yPanel.add(bt4);
frame.add(yPanel, BorderLayout.PAGE_START);
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
}构造参数说明
两个参数:分别是设置布局的组件对象,布局中组件的排列方式
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容







所有评论(0)